Explain 1NF, 2NF, and 3NF Using Your Tables
Explain 1NF, 2NF, and 3NF Using Your Tables
Table: StudentCourses (Before 1NF)
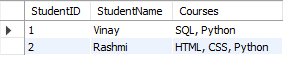
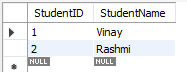
Table: Students (2NF)
Students Table:
Query Explanation:
-
Step 1: We create the
StudentCoursestable and insert data, where multiple courses are stored in a single column for each student. This violates the 1NF rule of atomicity. -
Step 2: We convert the table into 1NF by creating the
StudentCourses_1NFtable, where each course is placed in a separate row for each student, ensuring that every column contains atomic values. -
Step 3: We create a separate
Studentstable to eliminate partial dependency and meet the requirements of 2NF. In this step, we ensure thatStudentNamedepends solely onStudentID(not on the courses). -
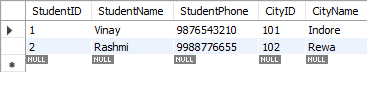
Step 4: The
StudentCoursetable is created to establish a many-to-many relationship betweenStudentIDandCourse. This helps meet the 2NF requirement, as the primary key is a combination ofStudentIDandCourse. -
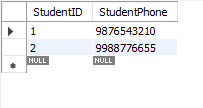
Step 5: The
StudentPhones_3NFtable is created, where student phone numbers are stored separately to remove any transitive dependency betweenStudentPhoneand other non-key attributes. This ensures that the table is in 3NF.
Result:
You can copy-paste this entire block and run it in your SQL editor to create and populate the tables for 1NF, 2NF, and 3NF in one go.
SQL Query:
-- Step 1: Creating the original table (StudentCourses)
CREATE TABLE StudentCourses (
StudentID INT,
StudentName VARCHAR(50),
Courses VARCHAR(100)
);
-- Inserting sample data into StudentCourses table
INSERT INTO StudentCourses VALUES
(1, 'Vinay', 'SQL, Python'),
(2, 'Rashmi', 'HTML, CSS, Python');
-- Step 2: Creating the StudentCourses_1NF table to convert to 1NF
CREATE TABLE StudentCourses_1NF (
StudentID INT,
StudentName VARCHAR(50),
Course VARCHAR(50)
);
-- Inserting data into StudentCourses_1NF
INSERT INTO StudentCourses_1NF VALUES
(1, 'Vinay', 'SQL'),
(1, 'Vinay', 'Python'),
(2, 'Rashmi', 'HTML'),
(2, 'Rashmi', 'CSS'),
(2, 'Rashmi', 'Python');
-- Step 3: Create Students table for 2NF
CREATE TABLE Students (
StudentID INT PRIMARY KEY,
StudentName VARCHAR(50)
);
-- Inserting data into Students table
INSERT INTO Students VALUES
(1, 'Vinay'),
(2, 'Rashmi');
-- Step 4: Create StudentCourse table for 2NF
CREATE TABLE StudentCourse (
StudentID INT,
Course VARCHAR(50),
PRIMARY KEY (StudentID, Course),
FOREIGN KEY (StudentID) REFERENCES Students(StudentID)
);
-- Inserting data into StudentCourse table
INSERT INTO StudentCourse VALUES
(1, 'SQL'),
(1, 'Python'),
(2, 'HTML'),
(2, 'CSS'),
(2, 'Python');
-- Step 5: Create StudentPhones_3NF table for 3NF (StudentPhone in a separate table)
CREATE TABLE StudentPhones_3NF (
StudentID INT PRIMARY KEY,
StudentPhone VARCHAR(15),
FOREIGN KEY (StudentID) REFERENCES StudentCourses_1NF(StudentID)
);
-- Inserting data into StudentPhones_3NF table
INSERT INTO StudentPhones_3NF (StudentID, StudentPhone)
SELECT StudentID, '9876543210' FROM StudentCourses_1NF WHERE StudentID = 1;
INSERT INTO StudentPhones_3NF (StudentID, StudentPhone)
SELECT StudentID, '9988776655' FROM StudentCourses_1NF WHERE StudentID = 2;
Output:
Converted Table: StudentCourses_1NF

Table: StudentCourse (2NF):
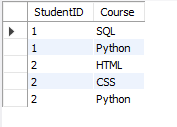
Table: StudentPhones_3NF